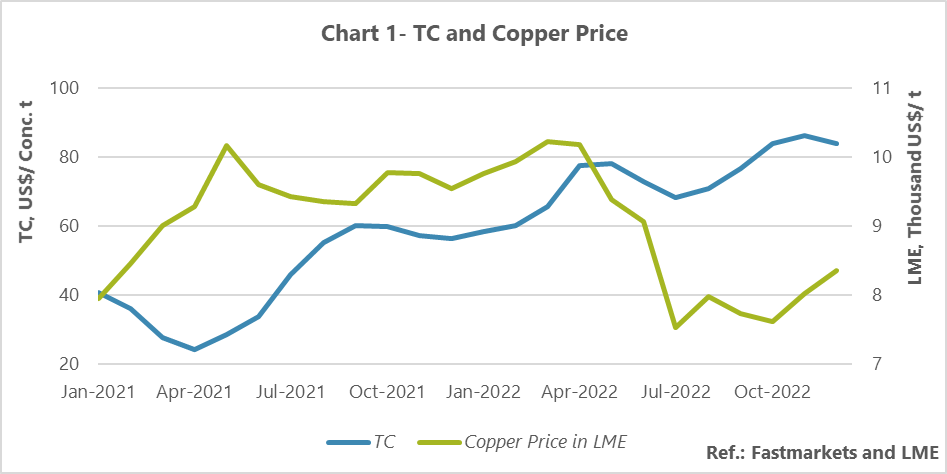
It’s worth mentioning that during the first quarter of 2021, TC decreased by a 17% average monthly rate and recorded the least amount of the recent decade. With the help of Chinese smelters’ closing down and demands dropping, TC increased, and over the last quarter of 2022, owing to the shortage of concentrate supply without any changes it remained at high levels.
Key mines of Chile and Peru faced production disruptions due to heavy rains and indigenous protests, and this matter caused a drop in production and exacerbating the supply deficit of copper concentrate in Indonesia’s mines last year. Therefore, the drop in concentrate production was one of the crucial reasons for TC’s upward trend all over 2022.
TC and RC constitute a monumental part of smelters’ income; it should be said that its share of these units’ income can be changeable in the range of 30% to over 70% due to the price of copper and sulfuric acid in the market, cathode premium and strictness about pollution emissions. Generally, the highest TC and RC levels are the amounts which miners accept forward integration as an economical way; because the high levels of them lead to a drop in miners’ profit. Besides, TC and RC would not remain at a level for a long time.
It’ll be a good point to say that owing to the fast growth of the smelting industry in China, forward integration of concentrate producer miners has decreased from 60% in the 1980s to 35% in the current decade. The focus of the smelting sector has been moved from Japan to China. Therefore, China has a remarkable role in the annual negotiations to determine TC and RC in view of ownership of more shares in the global smelting capacity.
Unprecedented TC Drop in 2021
The figure 1 indicates the average monthly TC of copper concentrate in the Asia Pacific region and copper price in LME during 2021 and 2022. In the last quarter of 2022, TC had no change, while it increased by 6% average monthly growth over the third quarter in 2022.
Since early November 2020, China forbade unofficial Australian copper concentrate import which caused pressure on Chinese smelters; also, this issue gave rise to the beginning of a downward trend in late 2020 and early 2021 in all over the world.
It’s worth mentioning that in the late 2020, the limited access to ships and containers induced delay in delivery of copper cathode seaborne and Shanghai’s custom inventory exceeded in the week ending December 28; because both the arbitrage window was still closed and customs clearance was reduced during the New Year holiday period; this matter prevented more drop in TC.
Mines’ production disruption and increase in smelting capacities created an extreme supply deficit in the first quarter of 2021 which led that during March and early April 2021, TC experiencing $24/t in the spot market which was its lowest level in the recent decade. After that, in the middle of April, TC almost remained constant and then faced an upward trend.
Over May 2021, TC continued to grow owing to the cathode supply deficit affected by the shutdowns caused by the maintenance of several smelters in China. TC reached from $24/t to $29/t in May 2021. Then with the help of the continuation of its uptrend could reach over $60/t in late 2021 and this amount was the highest level of TC in 2021.
Supply Deficit of Copper Concentrate in view of Production Disruption
In early 2022, huge volume of copper concentrates in smelters’ inventory, operation of new mines, Chinese holiday, and restricted transactions in the spot market are TC growth drivers at year’s first quarter. TC was chosen in the high level of $58/t in January and reached a level of $77/t in April.
During the months of March to May, TC could find a high level due to holidays caused by maintenance of Chinese smelters; in a way that TC could reach a level of over $78/t in May and record its first price summit in 2022. Then, as the result of smelters’ maintenance completion and the start of their activities and also, the increase in concentrate demand, TC began to fall.
The production disruption in key mines of Chile, Peru, and Panama increased the concern of smelters about the accessibility to copper concentrate.in Peru, protesting indigenous caused long-term disruptions in the country’s mines and limited access to South American concentrates. Besides, heavy rains in Indonesia made a tonnage reduction in this country and made more concern about copper concentrate supply deficit. Moreover, as a consequence of a large fire in Ventanas port, Chile which caused delay in copper concentrates seaborne transport; this matter toughen up concerns about access to copper concentrate and led to a decrease in TC.
The re-invasion of Covid-19 in China and the strictness of this country regarding the implementation of the zero-Covid policy caused a number smelters closure and reduced the copper concentrate demand. In addition, the sulfur price drop in China is another affecting factor on smelters’ concentrate demands; because a drop in sulfur price leads to a decrease in sulfuric acid as well and resulting in a fall of smelters’ income.
In December 2022, TC dropped owing to limited concentrate tonnage was supplied in the spot market by the miners and they were worried about the short-term accessibility of concentrate due to mineral supply risks, including export challenges due to the social challenges of the Southern Corridor of Peru and the Ventanas port fire. Also, China’s sudden exit from zero-Covid Policy had a positive effect on concentrate demand and made a reduction in TC.
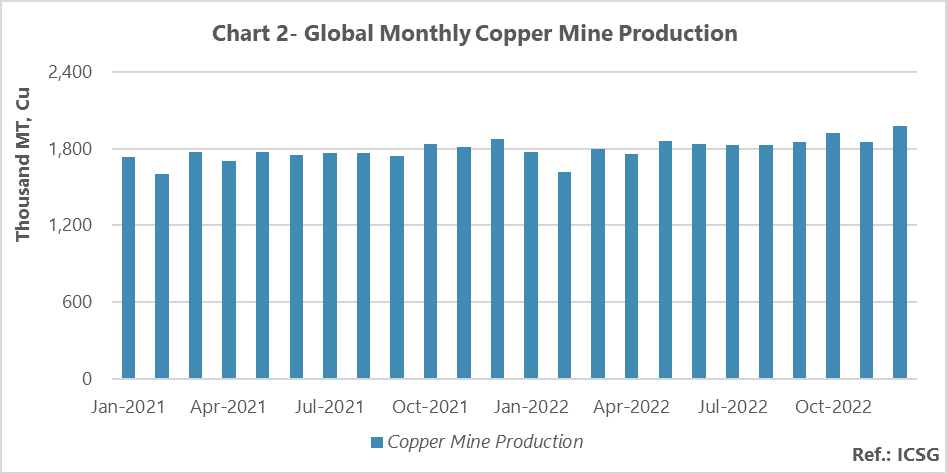
The figure 2 shows copper monthly production in the world in 2021 and 2022. Considering the fact that concentrates’ market balance has effect on TC’s trend, decrease in production owing to heavy disruption and increase in demand due to the development of smelting capacity in China, it can decrease TC.
Thanks to the new projects, the growth of smelters’ capacity will be continued in China and consequently, concentrate demand will be increased, too. Out of China’s borders, especially in Africa, Indonesia, and India there’s significant progress in the copper industry which makes the rivalry for copper concentrate and toughen up its supply deficit. Hence, the possibility of reducing TC is strengthened by the intensification of the supply deficit.