Following the growth of lithium batteries that are consumed in the electric vehicle industry, the production and trade of lithium metal has undergone significant changes and the largest share of the production of this metal in the world belongs to Australia; while most lithium reserves are found in Bolivia.
The global volume of lithium reserves is reported to be around 22Mt in 2021, and the largest reserves of this element are located in the countries known as the lithium triangle. It is worth mentioning that, South Korea and China are the largest global importer and exporter of lithium, respectively. The application of this metal, which is light and has superconducting properties, is mostly in the field of rechargeable batteries. Due to the market growth of electric and consumer vehicles in which lithium is used in the batteries of these vehicles, the production volume and its demand is expected to increase over the coming years.
Lithium is an element whose name comes from the Greek word lithos, which means stone. The reason for naming this element is the presence of a small amount of lithium element in most minerals (ores). This element is known as the lightest flare and the lowest density solid element under standard conditions of temperature and pressure. Due to the high reactivity of lithium, it cannot be found as a free element in nature; rather, it is always found in a part of a chemical compound, which is often an ionic compound. Lithium is found in the combination of spodumene, petalite, lepidolite, and amblygonite minerals. Since it dissolves in water, it can be seen in the form of ions and salts in ocean water as well.
The most obscure application of lithium is in rechargeable batteries in electronic devices; Lithium is also used in some non-rechargeable batteries for devices such as pacemakers, scratch games, and clocks. Lithium minerals are consumed directly as ore concentrates in ceramic and glass applications. Lithium metal in combination with aluminum and magnesium turns into alloys that have higher strength than these two metals and are lighter. A type of magnesium-lithium alloy is used in armor plating. Aluminum-lithium alloys are generally consumed in airplanes, bicycle frames, and high-speed trains.
Although the three lithium consuming industries differ by geographic location; but in general, in global markets, the end-use of lithium is 71% in the production of batteries, 14% in ceramics and glass, 4% in lubricants, 2% in flux powders used in continuous casting, 2% in polymers, 1% was reported in air purification and 6% in other industries.
Lithium reserves growth due to extensive global discoveries
Due to the extensive discoveries that have been made for this element over recent years, the identified lithium resources have increased significantly in the world. The global identified resources of lithium have been declared to be around 93Mt in 2021, of which 22Mt are reported as firm reserves of lithium in the world. Most of these reserves are located in Bolivia, Argentina, Australia, China, and Congo. It should be noted that, the global recoverable lithium reserves increased from 13Mt in 2012 to 22Mt in 2021, put it another way, the volume of lithium reserves has increased by 6% annually.
The center of lithium mining in the world; Lithium triangle
More than 75% of the global lithium resources are located in the lithium triangle located in Bolivia, Argentina, and Chile. Argentina ranks second in terms of lithium resources with 2.2Mt of lithium after Bolivia. After Argentina, Chile, Australia, the US, and China are in the next ranks. It is estimated that Argentina has approximately 10% of the total lithium resources. The two areas of Antorcha and Incahuasi are the centers of lithium mining in Argentina.
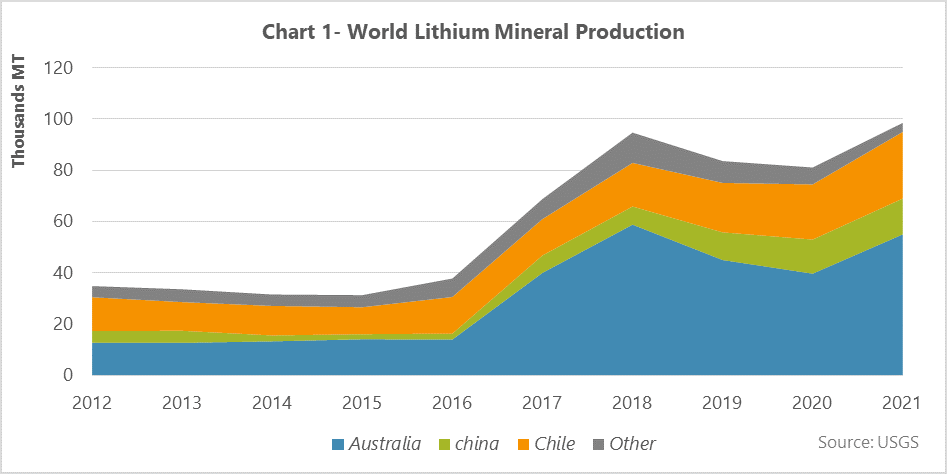
In order to investigate the global production of lithium mineral, the information published by the US Geological Survey was evaluated in the period from 2012 to 2021, and the results are indicated in Figure 1.
The global production of lithium mineral has been accompanied by a significant growth over the timeframe, from 35kt in 2012 to 100kt in 2021, according to the Figure 1. In other words, about 12.3% has been added to the global lithium mineral production annually, in which Australia, Chile, and China were the main producers with a share of 55%, 26%, and 14% of the global production.
The production of lithium decreased significantly in 2019 and one of the main reasons for this can be attributed to the reduction of China’s subsidies in the electric vehicle industry, according to the Figure 1, consequently the product’s consumption and production declined sharply. Furthermore, the global production of lithium drop by 5% in 2020, which the oversupply of lithium and the decrease in its price were the main reasons. Meanwhile, the consumption of lithium was 56kt in 2020, which is almost the same as in 2019 according to the United States Geological Survey report. It should be noted that despite the low demand for lithium in the q1 2020 due to the Covid-19 outbreak and the rapid growth of the lithium-ion battery market, this downward trend has been compensated in the second half of the same year.
Despite having a lot of lithium resources, Argentina has not yet been able to consolidate its position in the market. The production volume of lithium has decreased in the country from 2018 to 2020. The pandemic had a great impact on reducing the exploitation of lithium mines in Argentina, and therefore the country tried to escalate its lithium production capacity in 2021 by attracting foreign investment and achieved success in this regard with a production capacity up to 300kt.
The trade upward trend following the demand growth
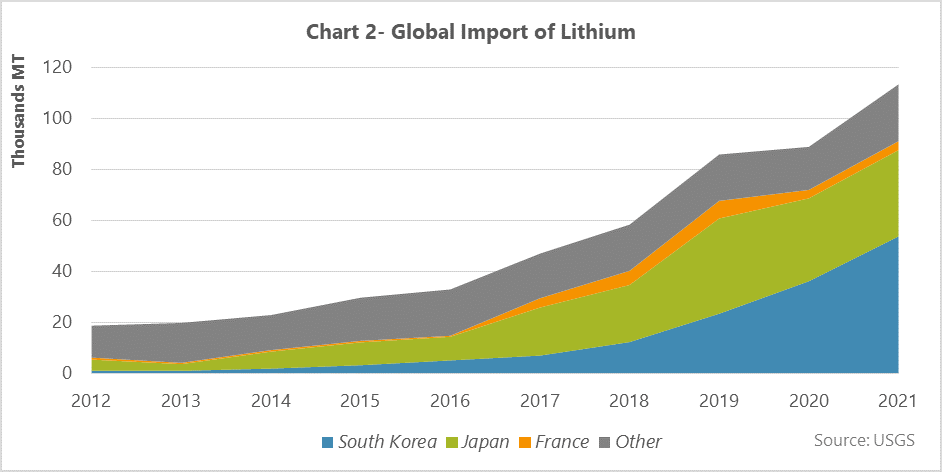
In order to investigate the global trade trend, the import of lithium and lithium hydrogen bound with the tariff code 282520 was investigated from 2012 to 2021 and the results are displayed in Figure 2.
Moreover, countries that are leaders in the field of industry and auto production have a greater share of lithium imports as in Figure 2. Because the lithium consumption in these countries is higher due to the production of lithium batteries. The import trend of lithium was up warded over the timeframe, which has increased by 18% annually from 25Mt in 2012 to 113Mt in 2021, as in Figure 2.
South Korea, Japan, and France each have a share of 47%, 29%, and 3% of the product global import, respectively. In addition with higher activity of industrial plants after passing through the production crisis caused by Covid-19, the global demand for lithium increased by 48% from 2020 to 2021, and as a result, the trade has been affected and grew by 24%.
The export trend of lithium is similar to its import over the period, increased from 21kt in 2012 to 107kt in 2021. In addition, the product’s export volume has been increased by about 20% annually. China, Chile, the US, and Russia were the main global lithium exporters, which has a share of 61%, 10.6%, 7.8%, and 7.7%, respectively.
Considering the supplication of lithium in the manufacturing of rechargeable batteries, in the electric vehicle industry and the rapid growth of the market over the recent years, the production trend of lithium and its supply is expected to increase over the coming years.